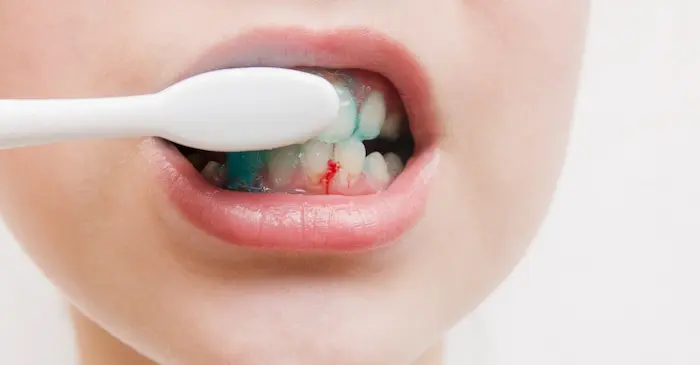
Bleeding gums is a common health problem that many people experience and is often associated with inflammation of the gums. This condition is generally considered a symptom of gum disease. The main factors causing bleeding gums include improper dental care routines, plaque buildup, and gum disease.
What Causes Bleeding Gums?
Incorrect or Insufficient Oral Care: Not brushing your teeth regularly and not flossing can lead to plaque buildup and then tartar (calculus) formation. Plaque is a sticky layer of bacteria that builds up at the gum line and can cause gingivitis (inflammation of the gums) and bleeding when it builds up.
- Gingivitis: This is characterized by redness, swelling, and easy bleeding of the gums when brushing or flossing. Gingivitis can lead to more serious gum disease if left untreated.
- Periodontitis: The advanced form of gingivitis, periodontitis causes serious damage to the gums, the bones that support the teeth, and other structures. This can lead to more severe bleeding of the gums, tooth loss, and other serious health problems.
- Incorrect Brushing Technique: Using a toothbrush that is too hard or brushing your teeth too hard can damage your gums and cause bleeding.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Deficiencies in vitamin C and vitamin K in particular can negatively affect gum health and lead to bleeding.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal changes during pregnancy, puberty, and menopause can make the gums more sensitive and prone to bleeding.
- Side Effects of Medications: Some medications, such as blood thinners, antidepressants, and heart medications, can cause gum bleeding.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking or using tobacco products increases the risk of developing gum disease and can lead to gum bleeding.
- Diseases: Some systemic diseases, such as diabetes, cancer, and HIV/AIDS, can also affect gum health and cause bleeding.
5 Tips to Stop Bleeding Gums
There are several important steps you can take to stop and prevent gum bleeding. These steps can help both improve your daily oral care routine and protect your gum health:
1. Regular and Proper Oral Care
Brushing your teeth
Brush your teeth at least twice a day, morning and night, using a fluoride toothpaste.
Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and brush gently using circular motions.
Flossing
Floss at least once a day to clean between your teeth and below your gum line.
This helps remove plaque and food particles that your toothbrush can’t reach.
Mouthwash
Using an antiseptic mouthwash can reduce the amount of bacteria in your mouth and support gum health.
2. Healthy Diet
Balanced Diet
A diet rich in vitamins C and K, which support gum health, can help prevent gum bleeding.
Be sure to eat plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources.
Avoid Sugary and Acidic Drinks
Sugary and acidic foods and drinks can lead to tooth decay and gum disease.
Limit your consumption of these.
3. Avoid Smoking and Tobacco Products
Smoking and tobacco use are one of the biggest risk factors for gum disease.
Quitting these habits can significantly improve your gum health.
4. Regular Dental Visits
Visiting your dentist every 6 months for professional dental cleaning and checkups is important in preventing gum disease and early detection of existing problems.
5. Stress Management
Stress can increase your body’s inflammatory response and make you more susceptible to gum disease.
Stress management techniques and getting enough rest can improve your overall health and gum health.
Bleeding Gum Treatment Methods
The treatment of bleeding gums depends on the underlying causes. In general, the goal of bleeding gum treatment is to control infection, improve gum health, and prevent recurrent bleeding. Here are some treatment methods that can be used for bleeding gums:
1. Professional Dental Cleaning
Scaling and Root Planing
A dentist or dental hygienist uses special instruments to remove tartar (calculus) and plaque deposits.
This process removes hardened plaque that has built up above and below the gum line.
Polishing
The surface of the teeth is smoothed to make it difficult for plaque to re-form.
2. Good Oral Hygiene Practices
Your dentist can guide you on proper brushing and flossing techniques.
This helps prevent plaque buildup and reduce gum bleeding.
3. Medication Use
Antibiotics:
In the presence of infection, the dentist may prescribe antibiotics to control the infection.
Antiseptic Mouthwashes:
Antiseptic mouthwashes may be recommended to reduce the number of bacteria and lower the risk of infection.
4. Surgical Methods
Flap Surgery (Pocket Depth Reduction): In cases of severe gum disease, the dentist may lift the gums to reach deeper areas for tartar removal. Afterwards, the gums are sutured back into place.
Bone and Tissue Grafts: For patients with advanced gum disease, grafts may be used to regenerate lost bone or gum tissue.
5. Lifestyle Changes
- Avoiding smoking, eating healthily, and stress management can help improve your gum health.
- Eat healthily and regularly consume foods rich in vitamins C and A.
- Brush your teeth twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Use dental floss to clean between your teeth and remove plaque.
- Regularly visit your dentist for check-ups.
If you’re looking for an expert team for gum treatment in Istanbul, our dental clinic in Kadıköy, Alyans Clinic, is here with its specialist periodontologists.


